
Optimizing your link profile is necessary whether you’re working with a new SEO client or just acquired an existing website.
Yet, it can be difficult to know where to start, especially for sites with thousands of existing links.

Jumping in blind is never a good idea, so always kick things off with a backlink audit.
Auditing your site’s backlink profile will help you identify potentially harmful links (which you may want to disavow) and uncover new backlink opportunities.
When done correctly, analyzing your backlink profile can provide invaluable insights—but you need to know what you’re looking for.
With a bit of detective work, you will uncover:
- The websites that link to yours the most
- Which sites linking to yours have the highest DA scores
- Links coming from PBNs and other spammy sources
- Which content is performing the best
- Broken internal and external links (to fix them)
Stay tuned to learn how to conduct an in-depth backlink audit on any website.
What Is a Backlink Audit?
A backlink audit is a process whereby you review and evaluate all the backlinks pointing to your website.
The primary purpose of conducting a backlink audit is to gain valuable insights that can help you grow and maintain a healthy backlink profile, which is critical for improving your search engine rankings.
A backlink audit also involves analyzing the following:
🔗The linking website’s domain rating/authority score
🔗The linking website’s URL, domain, and IP address
🔗The piece of content they link to on your site
🔗The anchor text used for the link
🔗The web page containing the backlink (and if it’s relevant to the page it links to)
A backlink audit is often the first step in your link-building strategy, regardless of the website’s purpose or industry.
Why is that?
An audit is the best way to gauge the health of a website’s backlink profile. If you don’t start with an audit, you have no way of knowing if the website has potentially harmful links pointing at it that could cause a manual action from Google.
Additionally, backlink audits provide a whole host of other benefits, including:
✅ Grow your backlink profile: Who are the biggest fans of your site? In other words, which sites link to your content the most? You won’t know unless you do a backlink audit. Building relationships with sites that already like your content can be super powerful for your backlink profile.
✅ Keep your backlink profile healthy: Auditing your website’s backlinks is the best way to keep your link profile healthy, which is key to SEO success. Regular audits will help you identify spammy and toxic backlinks like paid links or links from PBNs (private blog networks).
✅ Track your progress: Are your link-building efforts paying off or not? You won’t know unless you examine your backlink profile. During an audit, you’ll discover your most effective link-building strategies, which will be helpful in refining your campaign.
✅ Get insight into competitor strategies: Backlink audits aren’t just for your website. You should plug competitor sites into whatever tool you use. Doing so will let you peek into their link-building techniques, and you may find some you want to copy. You may find valuable backlink opportunities by auditing your competitors (like finding a website in your niche that accepts guest posts).
How to Perform a Backlink Audit in 9 Steps
Step #1: Choose a backlink audit tool
Now that you know why backlink audits are worth the effort, it’s time to dive into your backlink profile to discover the good, the bad, and the ugly.
There are multiple tools you can use to audit your backlinks, including:
➡️ SEMrush: The Backlink Analytics tool lets site owners conduct an in-depth analysis of their backlinks, including each referring domain’s authority score, IP address, toxicity score, and many other factors.
➡️ Moz: Moz offers backlink audit services and Link Explorer, a free backlink audit tool enabling users to view their backlink’s anchor text, page authority score, domain authority score, and more.
➡️ Ahrefs: The Site Explorer feature offers comprehensive insights into a website’s backlink profile, including:
- Total number of backlinks and referring domains
- Anchor text distribution
- Link relevance and quality assessment
- Historical backlink data
- Ability to discover new link opportunities by analyzing competitor backlinks
| 💡Pro-tip: Don’t have the budget for Ahrefs?
Don’t worry! Ahrefs offers a free Backlink Checker tool for search engine optimizers who are eager to audit their links but don’t have the budget for the paid version. |
➡️ Google Search Console: The “Links” report in Google Search Console is good for starting a backlink audit. It gives you a list of sites linking to yours,your most popular pages, and a glimpse into the quality of your backlinks by showing top linking sites per page. GSC is a great starting point, but you’ll need additional tools that offer more detailed analysis and allow you to remove unwanted links.
Generate a list of backlinks
Before conducting an audit, export a complete list of your backlinks. The quickest and easiest way to do this is with Google Search Console (if you haven’t set up GSC for your site already, here’s how to do so).
- Log in to GSC and navigate to the “Links” tab on the left-hand sidebar.
- Once you’re at the Links Report, click on the “Export External Links” button at the page’s top-right corner. Decide whether to export the file as a CSV, Google Sheets, or Excel file and hit “Export.”
A manual backlink audit is entirely possible with this list—but it would be extremely time-consuming and complex. So, to make it easier, we’ll show you how to do a backlink audit in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer tool.
Step #2: Benchmark your website against competitors
Once you have chosen your backlink audit tool, benchmarking your website against your competitors is the next step. You want to see how your site stacks up regarding backlinks and other key SEO metrics.
Why benchmark?
It’s like knowing your starting point in a race. You need to see where you stand compared to your rivals, especially if you want to outrank them. If they have way more backlinks and referring domains, you have some catching up to do. Plus, benchmarking helps you understand your website’s strengths and weaknesses.
Assess your website’s performance
1. To get started, log in to Ahrefs and navigate to the Site Explorer tool at the top of the page:

2. Enter your website’s URL, and hit the “Search” button:
| 💡Pro-tip: Use both the ‘http+https’ option
We recommend using the ‘http+https’ option, as it will check both versions of your website. The ‘subdomains’ selection will analyze the entire domain and subdomain, which is the best way to get an accurate overview of your backlink profile. You also have the option to analyze exact URLs, specific paths, and domains (excluding any subdomains). |
3. From there, you’ll be directed to the “Overview” page:

Here, you’ll get to peek at all your crucial SEO metrics like:
ℹ️ Total number of backlinks: How many links point to your site?
ℹ️ Diversity of referring domains: How many unique websites link to yours?
ℹ️ Domain rating: A score showing your website’s overall authority.
ℹ️ Total number of keywords you rank for: The terms people use to find you in search.
ℹ️ Traffic by location: Where your visitors are coming from.
ℹ️ The ratio between dofollow links and nofollow links: The balance of links that help your rankings (do-follow) and those that don’t (no-follow).
The Overview screen is invaluable for quickly gauging the success of your link-building tactics. Think of it as the home base of your SEO strategy since you’ll frequently check it to monitor the progress of your efforts.
Notable metrics here include your total number of backlinks and referring domains. In our example, we have 168,000 backlinks coming from 6,100 unique domains.
However, you must compare your metrics to competitors to truly benchmark your performance.
Check how your competitors are performing
Now, let’s see how you measure up.
- On the “Overview” page, go to the “Competitors” tab and add the URLs of your main competitors. It’s set to “Metrics” by default, which charts out your organic traffic and referring domains over a set period (you can view increments of one month, six months, one year, etc.):
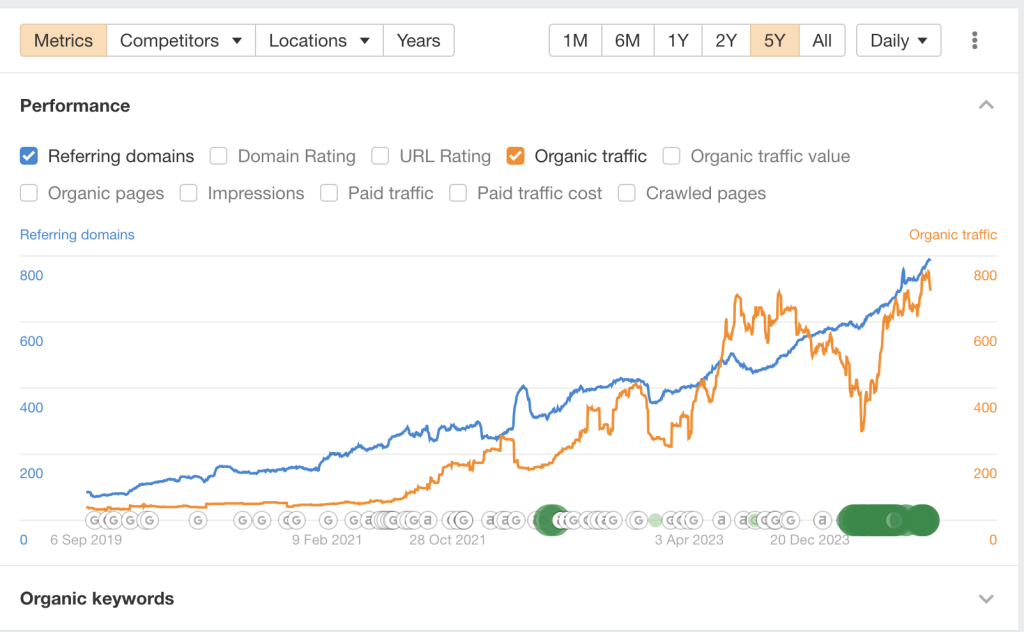
2. Click on the “Competitors” tab to add URLs for your competitors:

Once you’ve added a competitor, you’ll see charts directly comparing their SEO performance to yours.
3. Next, select “Backlink Profile” to compare your links directly:
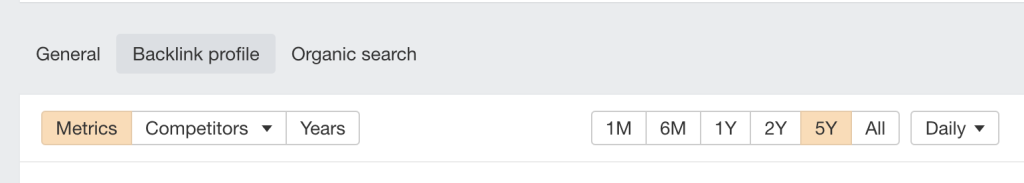
From here, you can view how you compare in terms of:
- Referring domains
- Domain rating
- New and lost referring domains
- Top-level domains
This will let you know whether there are any significant link gaps between you and your competitors, which is extremely useful.
Let’s look at a quick example:

As you can see here, the website marked orange has significantly more referring domains than the website marked blue. In this scenario, the blue site has an astronomical amount of link-building to do if they want to catch up.
However, the gap isn’t as wide regarding the website’s URL ratings. The orange site has a URL of 57, while the blue site has a URL rating of 30. Therefore, the blue site is lagging behind the orange site, but the gap isn’t as wide as the referring domains would suggest.
This suggests that although the first website has tons more backlinks, they aren’t better quality.
Finding competitors
Are you not sure who your top organic competitors are? Ahrefs has got you covered.
Navigate to the “General” tab and scroll down to “Top organic competitors.” This will provide a list of your closest competitors, any keyword overlap, and common keywords (which are keywords you’re both competing for).

This makes it easy to quickly identify websites competing for the same audience, which you can then mine to discover new backlink opportunities.
Step #3: Find out which content is performing the best
Next, it’s time to discover which pages on your site attract the most backlinks. This helps you see which content types—like videos, infographics, or how-to guides—perform well for earning inbound links and driving organic search traffic.
Why does this matter?
Knowing which content gets the most backlinks helps you focus on creating more of what works. For example, if videos are earning lots of links, producing more videos will help you build even more. Without this insight, you might waste time on content that doesn’t attract backlinks. Below, we’ll show you how to find your top-performing content on Ahrefs.
How to find top-performing content with Ahrefs
Enter your website’s URL in the Site Explorer search bar and click the “Search” button. This will give you an overview of your site’s performance. Look for the “Pages” report on the left-hand menu and select “Best by Links” underneath:

This will take you to a report that includes a detailed list of your most linked-to pages with 50 results per page. Ahrefs provides the following backlink information for each page:
- How many backlinks your site has
- Number of referring domains
- New backlinks gained
- Lost backlinks
- A breakdown of dofollow backlinks vs. nofollow links
- Number of redirects
The metrics above are all critical to consider when analyzing your top-performing content. For example, one of your web pages might have a lot of high-quality backlinks, but when you dig deeper, you find that most are nofollow links, which means they don’t help improve your SEO.
| 💡What is a “nofollow” link?
A no-follow link tells search engines not to pass on SEO value (also known as “link juice”) to the website it points to. In other words, when a link is marked as no-follow, it doesn’t help the linked page improve its search engine rankings. No-follow links have a lot of uses including preventing spam when the site owner doesn’t want to vouch for the linked content or in situations where links are user-generated, like in blog comments or forums. |
Another example is that you could have a page with tons of backlinks, but they all come from the same few websites. This is often a sign of private blog networks (PBNs)—a risky link-building tactic.
Let’s use our website as an example:
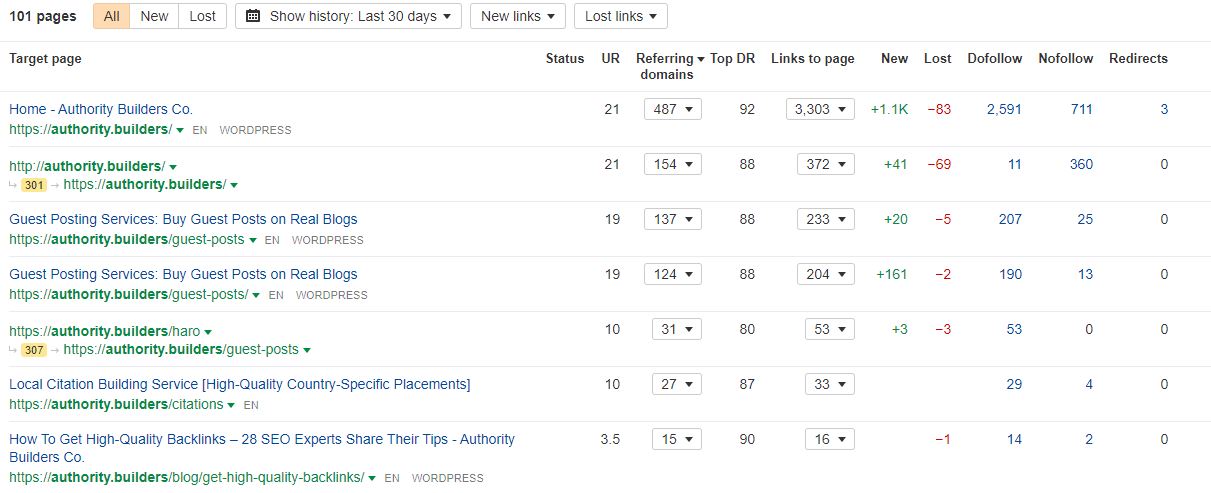
Our “Best by links” report shows that our home page is the most linked-to page (not too surprising), followed by numerous free SEO tools (rank checker, keyword planner, title generator, etc.).
For our website, it’s clear that our free SEO tools are generating backlinks left, right, and center. If this were your domain and you wanted to attract more organic backlinks, designing more free tools would be the way to go.
| 💡Pro-tip: Free tools are backlink magnets
Free tools are an excellent way to pick up quality backlinks and this doesn’t just apply to digital marketing efforts. Try to brainstorm helpful tools you can create for your audience. Day planners, calculators, and document templates are all viable free tool ideas that can help you bring more links to your website. |
Step #4: Refresh existing content that has untapped potential
Once you know which content types are putting in the most work for your backlink profile, it’s time to consider the flip side of the coin.
You need to look at your site’s backlink profile for pages that aren’t ranking well—they may contain many backlinks that don’t generate much traffic. These web pages have the most untapped potential.
Luckily, there is an easy way to find these pages, fix them, and hopefully boost traffic: Ahrefs’ Legacy Top Pages report. You’ll find it in the left-hand menu of Site Explorer, under the Legacy column.

This report displays your best-performing web pages in terms of ranking, traffic, etc. However, at this stage, we want to see pages with next-to-no traffic.
To filter the report this way, click on the “Traffic” icon so that the arrow next to it points up instead of down.
Now, your lowest-performing pages (traffic-wise) will appear at the top.
What you’re looking for now is pages with low traffic yet lots of referring domains, like this example:

This page has a high number of inbound links but generates very little traffic. If you spot something like this in your report, undiagnosed issues are likely causing this page to perform poorly in the SERPS.
Here are some possible reasons:
⚠️The web page contains outdated information that needs updating.
⚠️ Several on-page or technical SEO factors are holding the page back.
⚠️The content failed to satisfy the search intent of users, causing them to click back to the search results (a high bounce rate is a clue). If you want your web pages to succeed, you must consider the users’ search intent.
| 💡Pro-tip: What’s search intent?
Search intent is the “why” behind a user’s search – what they hope to find. There are four main types:
Failing to meet search intent leads to frustrated users. Always consider the user’s goal when targeting keywords. Keyword research tools can help you identify search intent. |
Lastly, it is essential to ensure that your on-page and technical SEO is on point for the pages in question. We’ll discuss how to do this in more detail below.
Step #5: Check for technical SEO issues
We mentioned above how technical problems with your website can hold back your page’s performance. This is such an important area that we need to discuss it in more detail. Technical SEO ensures your website’s structure and technical elements are in good shape so search engines can easily find and understand your content.
Factors like having the same content in multiple places, slow loading times, or leaving users confused when they try to navigate your site can all make it harder for your page to rank well.
It can get a little technical, but we’ll keep it simple and cover some of the main things to look out for when checking your backlinks.
Crawlability
Ensure search engines can access and crawl your website without any issues. Search engines can be blocked by misconfigurations in the robots.txt file, meta tags (e.g., noindex tags), or server errors that restrict crawlers from accessing the site. If a page isn’t crawled, then it cannot be found in a search.
To identify issues, look at Google Search Console’s Crawl Report. The report shows pages being crawled and any issues encountered, such as 404 errors, server errors, or pages excluded from indexing.
Indexability
Make sure that search engines index all critical pages.
✅ Best practice: Use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to check whether pages are indexed. Ensure there are no noindex tags on critical pages. If certain pages should not be indexed (like admin pages), use the noindex directive appropriately.
XML sitemap
Make sure that your XML sitemap includes all relevant pages and that it’s submitted to search engines.
✅ Best practice: Create and submit an XML sitemap to Google and Bing. Ensure it is automatically updated when you add new content. Your sitemap should only include important pages you want to be indexed and exclude duplicates or pages with “noindex.”
ℹ️ You can also submit an XML sitemap in Google Search Console.
Canonicalization
Verify that duplicate content issues are handled using canonical tags.
✅ Best practice: Use canonical tags to signal the preferred version of a page when you have duplicate or similar content. This helps prevent the dilution of link equity across multiple URLs and ensures search engines understand which version to index.
Mobile-friendliness
Make sure your site is optimized for mobile devices.
✅ Best practice: Regularly use Google Lighthouse to check whether your site works well on mobile. Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing, so your site should be responsive, with text, buttons, and images optimized for smaller screens.
Site speed
Check whether your site loads quickly, as slow pages can hurt both user experience and SEO rankings.
✅ Best practice: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to assess load times. Aim for a load time of under three seconds.
URL structure
Ensure URLs are clean, descriptive, and consistent across your site.
✅ Best practice: Use simple, readable URLs that include keywords when relevant. Avoid long, complex, or dynamically generated URLs. Implement 301 redirects for any outdated or removed pages to avoid 404 errors.
Broken links
Check for any broken internal or external links that lead to 404 errors.
✅ Best practice: Use tools like Ahrefs to identify broken links and fix them by updating URLs or setting up redirects. Regularly audit your site to ensure links are kept up-to-date.
👇🏼We’ll explain this in more detail in Step #7
Step #6 Improve on-page SEO
In addition to technical SEO, you’ll need to add checking your on-page SEO.
✅ Best practice: When auditing on-page SEO, you analyze individual web page’s content and HTML structure to ensure they are optimized for search engines and user experience. Here are some key issues you need to look at:
Title tags
The title tag of each page should be clear, descriptive, and include your main keyword.
✅ Best practice: Keep title tags between 50-60 characters, make them compelling, and ensure they reflect the page’s content. If possible, include your primary keyword naturally at the beginning.
Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions should briefly summarize the page’s content and entice users to click.
✅ Best practice: Keep meta descriptions between 150-160 characters and include the target keyword. Make sure it’s relevant and encourages users to click through to your site.
Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.)
Make sure each page has a clear structure by using header tags (H1 for the main heading, H2 for subheadings, etc.).
✅ Best practice: Use only one H1 tag that includes the main keyword per page. Use H2 and H3 tags for subheadings to organize your content logically. This helps both users and search engines understand the structure of the page.
Keyword usage
For each page, ensure your target keyword and its variations appear naturally in the text. Avoid keyword stuffing.
✅ Best practice: Aim for natural, relevant use of keywords in the title, headers, and body text. Include long-tail keywords and related phrases to make the content more comprehensive.
Internal linking
Check internal links that point to other relevant pages on your site.
✅ Best practice: Use internal links to guide users to other important pages and distribute authority across your website. Make sure your anchor text is descriptive and relevant.
Step #7: Identify and fix broken links (internal and external)
Broken links are a certainty that every website faces, and if you aren’t careful, they could harm your SEO efforts.
Why do links break?
There are dozens of reasons, including mistyped URLs, deleted pages, changes in site architecture, and domain name changes—just to name a few.
It’s common to find broken internal or external links, but they can negatively impact your SEO if left unaddressed.
Google prioritizes high-quality websites with accurate information. Numerous broken links might signal to Google that your website is neglected or outdated, affecting your rankings. Regular cleanup is key to maintaining a healthy website and strong SEO performance.
How to detect and fix broken internal links
There are a few ways you can go about this with Ahrefs, but we will stick with the Best by Links report because it’s the quickest and easiest way (and it has options to identify both internal and external broken links).
1. Enter your website’s URL in the Site Explorer search bar and click the “Search” button. Look for the “Pages” report on the left-hand menu and select “Best by Links” underneath:
2. Navigate to the “Internal Backlinks” option at the top of the page. By default, this report will show your internal pages that receive the most links.
3. Next, select “404 Not Found” under the “HTTP Code” filter option to display pages with broken links:
4. Click on “Show Results,” and you’ll get to see a list of all the broken internal backlinks on your website:
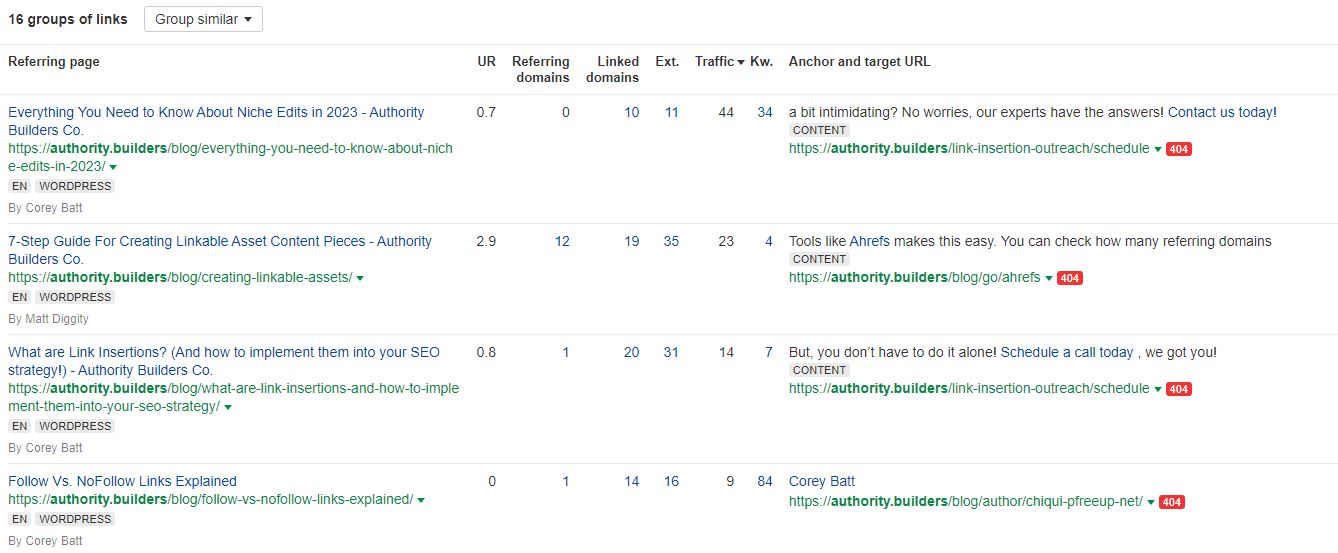
Correcting broken links on your web pages is crucial, especially for ones with lots of links pointing to them. Until you fix those broken links, all that link juice is going to waste.
The good news is fixing broken internal links is not too difficult. All you have to do is either:
1️⃣ Updating the URL to point to the correct page.
2️⃣ Removing the link if the page no longer exists.
How to detect and fix broken external links
Next, it’s time to check for broken external backlinks that could hinder your SEO. Select the “External Backlinks” tab. From there, select “404 Not Found” under the “HTTP Code” filter.
Now, you can view all your external backlinks that return 404 Not Found errors. Once again, all that precious link juice is wasted if the link points to a 404, so you should aim to correct these links ASAP.
Unfortunately, fixing broken external links isn’t as quick or easy as fixing internal links. You’ll have to contact other site owners to fix the link, which may take longer than you’d like.
Ideally, you’d want to get broken backlinks reinstated, which will restore the link juice and improve your SEO.
However, this isn’t always possible, as the page in question may no longer exist. In that case, contact the site owner and request that they remove the link instead.
| 💡Pro-tip: Manually check each link that Ahrefs claims is broken
No tool is 100% accurate all the time, so you should first confirm that a link is broken before contacting the site owner. |
Step #8: Disavow or manually remove any harmful links
Alright, let’s get back on track with the audit process.
The next crucial step is scrutinizing your backlink profile for potentially harmful links. These links can seriously damage your website’s reputation and search rankings in Google’s eyes.
Harmful links are backlinks that originate from low-quality, irrelevant, or spammy sites. They can signal to Google that your site is engaging in manipulative link-building practices, which can result in penalties or even complete removal from search results.
Here’s a breakdown of some common types of spammy backlinks:
⚠️PBNs (private blog networks): These are networks of interconnected websites created solely to pass on link authority to target sites. Google actively seeks out and penalizes PBNs.
⚠️Guest posts on low-quality sites: While guest posting can be a legitimate way to build backlinks, it becomes harmful when done on low-quality, irrelevant, or spammy websites.
⚠️Forum spam: This involves posting links to your site in irrelevant forums or discussions, often with generic or promotional anchor text.
⚠️Comment spam: Similar to forum spam, this involves posting links in blog comments or other online discussions, often with little or no relevance to the topic at hand.
⚠️Hidden links: This type of spammy backlink is intentionally hidden from users but visible to search engines. They are often used to manipulate search rankings.
⚠️Links from nonrelevant websites: Even if the linking site isn’t spammy, links from completely unrelated websites can be seen as unnatural and potentially harmful.
Now, go back to the list of backlinks you compiled earlier and visit each linking page. Carefully examine each link and the context in which it appears to determine whether any of these toxic backlink types are present.
If you identify any truly harmful links during your audit, or if your site has already been penalized due to manipulative links, you’ll need to use Google’s Disavow Tool to disavow them. We’ll show you how to do this below.
How to disavow backlinks
Disavowing links is essentially a way to tell Google, “Hey, I don’t want you to consider these specific links when evaluating my website’s authority and rankings.” It’s like cutting ties with those links, making them invisible to Google’s algorithm.
Google’s Disavow Tool is located within Google Search Console. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it:
- Log in to Google Search Console and select your “property type.”
- In the left-hand menu, navigate to “Links” and then click on “Disavow links.“
- You’ll see a warning message about the potential risks of disavowing links. Read it carefully and proceed only if you’re confident that disavowing is necessary.
- Click on the “Disavow links” button.
- Choose the .txt file containing the list of links you want to disavow. Ensure it’s formatted correctly according to Google’s specifications:
- Click “Submit” to upload the file.
| 💡Pro-tip: This is a last resort!
Disavowing links should only be used as a last resort when you’re sure the links harm your search performance. Disavowing links should be your last resort, not your first line of defense. Misusing this tool can have negative consequences, potentially further harming your rankings. Google’s algorithm is sophisticated enough to automatically identify and discount most low-quality links. |
Step #9: Regularly monitor your backlink profile
By now, you’ve completed a full backlink audit and disavowed any harmful links. Well done!
The final step, however, is to monitor your backlink profile periodically to catch any major changes before they get a chance to cause issues.
How often you monitor your profile will depend on your website’s activity and your niche’s competitiveness.
If your site sees a ton of traffic each day and your niche is fiercely competitive, you should review your link profile once every two weeks. If your site is less busy, then reviewing your links once per month should suffice. As for full backlink audits, you should knock one out every few months (or sooner).
Monitoring your link profile is crucial for the following reasons:
Detecting new links
Link-building is an ongoing process, and your team (or the agency you use) will be conducting outreach constantly to acquire new links. Accordingly, you need a way to detect any new links you pick up. Ahrefs’ Backlinks Alert is perfect for this.
An email notification goes out whenever your chosen domain, subdomain, subfolder, or URL gains or loses a backlink. This makes it extremely easy to keep track of your current link-building efforts.
Monitoring negative SEO
While their effectiveness is debated (Google claims negative SEO attacks have no effect), negative SEO attacks are a very real thing. This happens when a competing website floods your site with tons of spammy links, hoping to derail your search rankings. By closely monitoring your backlink profile, you can catch negative SEO attacks as soon as they occur.
Managing broken links
As stated before, broken links happen all the time, and they affect virtually every website. That’s why it’s important to keep an eye on your backlink profile to ensure that you don’t accrue too many broken links.
Competitor insights
You never know when one of your competitors may stumble upon a backlink goldmine. If you keep a close eye on their backlink profile (in comparison to yours), you’ll be able to capitalize on any new backlink opportunities they find.
Take Your Backlink Profile to the Next Level with Authority Builders
Conducting a backlink audit is by no means a simple or quick process. As you can probably tell by now, it’s a time-intensive, complex endeavor. If you’re running a business, it’s unlikely that you’d have the time to audit your backlink profile.
Authority Builders Link Audits will take this integral process off your hands, and we’ll provide you with a perfectly formatted disavow file to ensure the health of your backlink profile.
We also offer custom link-building campaigns through ABC Plus, so don’t delay and sign up today.
